Learning and Development Strategies in HRM.
Learning and development strategies are crucial if an organization wants a long-term success and growth in today’s changing business landscape. It sets out the workforce capabilities, skills and competencies the organization needs, and how they can developed to ensure a sustainable, successful organization
"A collection of organized initiatives by an
organization aimed at enhancing job-related knowledge, skills, attitudes, and
social behavior to attain specific objectives associated with a particular job
or role.
HRM has evolved significantly over years, expanding beyond
its administrative functions to become a strategic driver of organizational
success. Among the fundamental roles HRM plays, the emphasis on Learning and
Development strategies stands out as a crucial element in fostering employee
growth and organizational advancement.
Importance of
Learning and Development in HRM.
According to
Learning and development strategies within HRM are vital as
they contribute to enhancing employee’s skills, knowledge, and capabilities,
aligning them with the organizational targets and goals. Furthermore, Learning
and development initiatives cultivate a culture of continuous learning,
promoting employee engagement, retention and overall productivity
Different Learning
Styles in Learning and Development
Several theories support the implementation of effective
Learning and development strategies within Human Resource Management. The seven
learning styles theory suggests that individuals respond best to different
styles of learning, each focusing on one of the five senses or involving a
social aspect. Tailoring teaching to these styles can improve efficiency and
retention of information
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Furthermore, according to Kolb’s Experiential Learning
Theory
Bandura’s Social
Learning Theory and Social Cognitive Learning Theory
Albert Bandura’s, father of cognitive theory emphasizes
observational learning and the role of modeling in acquiring behaviors and skills.
His Social Cognitive theory has impacted several fields of study, including
psychotherapy, social policy, health sciences, and education.
The Social Learning Theory (SLT) is recognized as a vital aspect of sustainable natural resource management and facilitating positive behavioral changes
In today's workplaces, mentorship programs and peer learning
initiatives reflect Bandura's theory. Employees learn through observing
experienced colleagues, mimicking their actions, and gaining expertise through
shared experiences. This theory underpins the effectiveness of role modeling
and social interactions in skill acquisition.
Kolb’s Learning
Theory
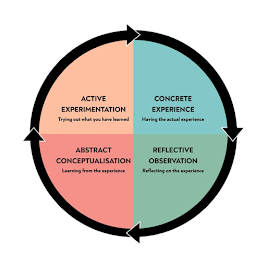
Similarly, Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory highlights
the cyclical nature of learning through concrete experiences, reflective observation,
abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. In modern HRM
practices, this theory is evident in immersive training workshops, where
employees engage in hands-on experiences, reflect on their actions,
conceptualize their learning, and apply new insights to their roles. For
instance, tech companies often use hackathons or innovation labs, fostering
learning by doing and iterative learning cycles, aligning with Kolb's theory
2. Reflective Observation: learner reflects on new
experience in light of their existing knowledge.
3. Abstract Conceptualization: people learned from their
past experience.
4. Active Experimentation: the learner applies ideas and
trying out what have learned and modifies concepts gives rise to experimental
These theories offer HRM practitioners frameworks to design
training programs that cater to diverse learning styles and preferences. By
integrating Bandura's emphasis on observation and modeling or Kolb's experiential
learning cycles, HRM can create more comprehensive and effective learning
experiences tailored to individual employee needs and organizational goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Learning and Development strategies play a
pivotal role in HRM, contributing significantly to organizational growth and
employee satisfaction. By implementing theories like Social Learning and
Experiential Learning, HRM can design effective L&D programs. Real-world
examples from companies like Google and IBM demonstrate the tangible benefits
of investing in robust L&D strategies.
In essence, understanding the theoretical underpinnings is
crucial in comprehending human activities. The evolution of educational
sciences and psychological theories has significantly contributed to the
advancement of learning and development theories. Choosing the right theory is
instrumental in strategic planning, guiding specific outcomes. Particularly in
the realm of organizational performance, where human capital plays a pivotal
role, learning theories play a decisive role in planning strategic training
initiatives. Aligning employees' professional growth with company goals is
essential for competitive advantage. Continuous education fostered by HRM
within the workplace not only develops employees personally and professionally
but also boosts organizational productivity. The various learning theories like
behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and connectives offer diverse
approaches for HRM training implementation. The apt selection or combination of
these theories determines a company's success in achieving both present and
future objectives
References
Aguinis, H. & Kraiger, K., 2009. Benefits of
Training and Development for Individuals and Teams, Organizations, and
Society.. Annual Review of Psychology, Volume 60, pp. 451-474.
Bandura, A.,
1997. Social Learning Theory. Englewood Cliffs : NJ: Prentice Hall.
C.L.V, T.
& S.L, B., 2016. Learning, development, and training: The influence of
synergies through educational evolution.. International Journal of Adult
Vocational Education and Technology, 7(4), pp. 85-104.
CIPD, 2023. Explore
how to create and implement a learning and development strategy and policy to
support organisational performance. [Online]
Available at: https://www.cipd.org/en/knowledge/factsheets/strategy-development-factsheet/
[Accessed 13 December 2023].
CIPD, 2023. What
are the 7 different learning styles and do they work?. [Online]
Available at: https://www.avadolearning.com/blog/the-7-different-learning-styles-and-what-they-mean/#:~:text=These%20are%20split%20into%20spatial,5%20percent%20are%20kinaesthetic%20learners.
[Accessed 16 December 2023].
Henderson,
M., 2017. What works and why? Student perceptions of ‘useful’ digital
technology in university teaching and learning. studies in Higher
Education, 42(8), pp. 1-13.
Jeffrey , P.
& Muro , M., 2008. A critical review of the theory and application of
social learning in participatory natural resource management processes. Journal
of environmental planning and management , 51(3), pp. 325-344.
Kolb, D. A.,
1984. Experiential Learning: Experience As The Source Of Learning And
Development. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Mcleod, S.,
2023. Kolb’s Learning Styles And Experiential Learning Cycle. [Online]
Available at: https://www.simplypsychology.org/learning-kolb.html
[Accessed 16 December 2023].
Symonds, C.,
2023. What is the Role of HR in Learning and Development (L&D)?. [Online]
Available at: https://factorialhr.com/blog/learning-and-development/#what-hr
[Accessed 13 December 2023].


Yes there are different learning methodologies but it is essential to select the proper model according to the employees. Learning theories is important. However Before designing any training program, HRM should first identify the learning styles of employees. This can be done through assessments or surveys. Understanding the learning styles of employees can help training managers change their training style.
ReplyDeleteAbsolutely, I completely agree. Tailoring learning methodologies to suit the diverse learning styles of employees is crucial for effective training outcomes. Recognizing and aligning with various learning theories is fundamental, but the real value lies in HRM's ability to ascertain the specific learning styles of their workforce. By utilizing assessments or surveys to understand these styles, training managers can adeptly adapt their approaches, ensuring that the training programs resonate and cater to individual preferences, ultimately maximizing the impact of the learning experience.
DeleteAgreed. Also it is important to understand that there are different types of learners which is denoted through the VARK learning styles where some employees may prefer Visual, Audio, Reading/Writing and Kinesthetic or at time a combination of a few of there learning styles. Hence, it is important to cater to a majority of the learning styles when either organizing or offering trainings from L&D.
ReplyDeleteAbsolutely Rushini, recognizing diverse learning styles, as illustrated by the VARK model, is crucial in designing effective training programs. Tailoring content to encompass Visual, Audio, Reading/Writing, and Kinesthetic preferences ensures a more inclusive and impactful learning experience for a broader spectrum of employees. Adapting training methodologies to accommodate various learning styles significantly enhances engagement and knowledge retention, fostering a more dynamic and comprehensive learning environment within L&D initiatives.
DeleteThanks for the share. While many learning theories exist , I feel no one theory would address an organization's learning requirements as a whole and it would have to be tailor made according to the organizations need at the time.
ReplyDeleteAbsolutely true Rehana. Learning theories offer valuable frameworks, but their universal application to address an organization's diverse learning needs might fall short. Customizing a learning approach according to specific organizational requirements at any given moment seems imperative. It's about amalgamating the best aspects of various theories and adapting them to create a tailored learning strategy that best suits the organization's dynamic needs and goals.
DeleteLearning and Development is one of the key responsibilities of HR section in every company. Many of the larger organizations, the development plan for personnel is managed by a selected L&D position or department (Rao, 2016).
ReplyDeleteAbsolutely, Learning and Development (L&D) stands as a core responsibility within HR across companies. In larger organizations, dedicated L&D positions or departments play a pivotal role in crafting and managing personnel development plans, ensuring a structured approach to employee growth and skill enhancement.
DeleteYou have taken a valuble topic of current period. A learning and development (L&D) strategy outlines how an organisation develops its workforce's capabilities, skills and competencies. It’s a key part of the overall business strategy.
ReplyDeleteAbsolutely, Learning and Development (L&D) stands as a core responsibility within HR across companies. In larger organizations, dedicated L&D positions or departments play a pivotal role in crafting and managing personnel development plans, ensuring a structured approach to employee growth and skill enhancement. Thank you Bagya for your valuable comment.
DeleteAgreed. Learning and development is part and partial content of any company. As mangers need mor focus on the same
ReplyDeleteThat being stated, immediate supervisors must to take the initiative to inquire about their staff members' development objectives. By suggesting learning and development initiatives that might be a suitable fit for their team members, managers can take on a champion role for the professional growth and development of their staff.
ReplyDeleteEmployees should also be accountable for their own personal growth and learning. Workers should be proactive in looking for and applying to the best learning opportunities for them by determining where they are.